Poison Sumac
General:
Poison sumac – Toxicodendron Vernix, grows in swamps, bogs, depressions, and other wet areas. Like both poison ivy and poison oak, poison sumac produces urushiol, a clear liquid compound found within the sap of the plant that causes an itching rash in most people who touch it.
Poison sumac basically manifests itself as a woody shrub or small tree. Unlike both poison ivy and poison oak, poison sumac is not an overly common plant.
Identification:
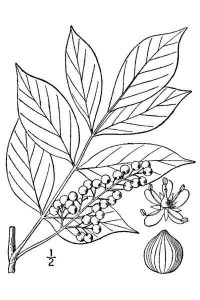
Poison sumac is a woody shrub or a small, slender tree that measures 5′-20′ tall. The leaves are pinnately compound (meaning – the leaflets grow from several places along the stalk) and alternate along the stem. The plant is deciduous so the leaves fall in the autumn turning brilliant orange to red in color. Each leaf stem contains 7 to 15 leaflets that are usually 2″ to 4″ long and 1″ to 2″ wide, and elliptic
to oblong in outline. The lower leaf surface is lighter green and the edges are smooth (not toothed). The central leaf stalk is typically reddish colored.
New stems are smooth and reddish, but they gradually turn tan to light gray with age. These light-colored leafless stems can look deceptively like other non-toxic shrubs or trees during the winter. Small greenish flowers are followed by white berries similar to poison ivy.
Location:
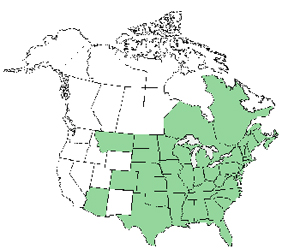
As can be seen in the map, poison sumac is found in most of the eastern United States, between Texas and Florida in the south, to Minnesota and Quebec in the north. Poison sumac is generally found in wet soil. The picture above was taken at the University of Michigan – Nichols Arboretum in Ann Arbor, MI. It was on the side of a hill in very wet soil.
Poison: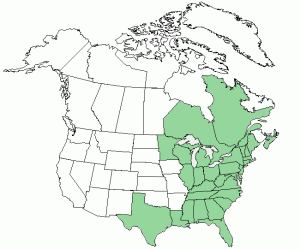
Urushiol binds to the skin on contact, where it causes severe itching that often develops into a red rash or flesh colored bumps and blistering. The rash can be treated with Calamine lotion or other over the counter remedies such as oatmeal baths and baking soda. In severe cases hospitalization may be required or if the plant has been ingested.
Urushiol oil can remain active for several years, so handling dead leaves or vines can cause a reaction. In addition, oil transferred from the plant to other objects (such as pet fur) can cause the rash if it comes into contact with the skin.
The fluids released by scratching the blisters do not spread the poison or the rash. The fluid in the blisters is produced by the body and it is not by urushiol.